Polarizer Selection Guide
*You can click the below product name to new tab and view more details
Polarizer |
Material |
Light Path |
Feature |
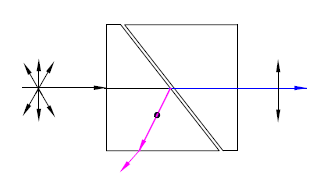
Glan-Taylor Prism Polarizer |
Calcite(350~2300nm)α-BBO(190~3500nm)YVO4 (500~4000nm) |
|
Air-SpacedNear Brewster CuttingNot applicable for high Damage energy |
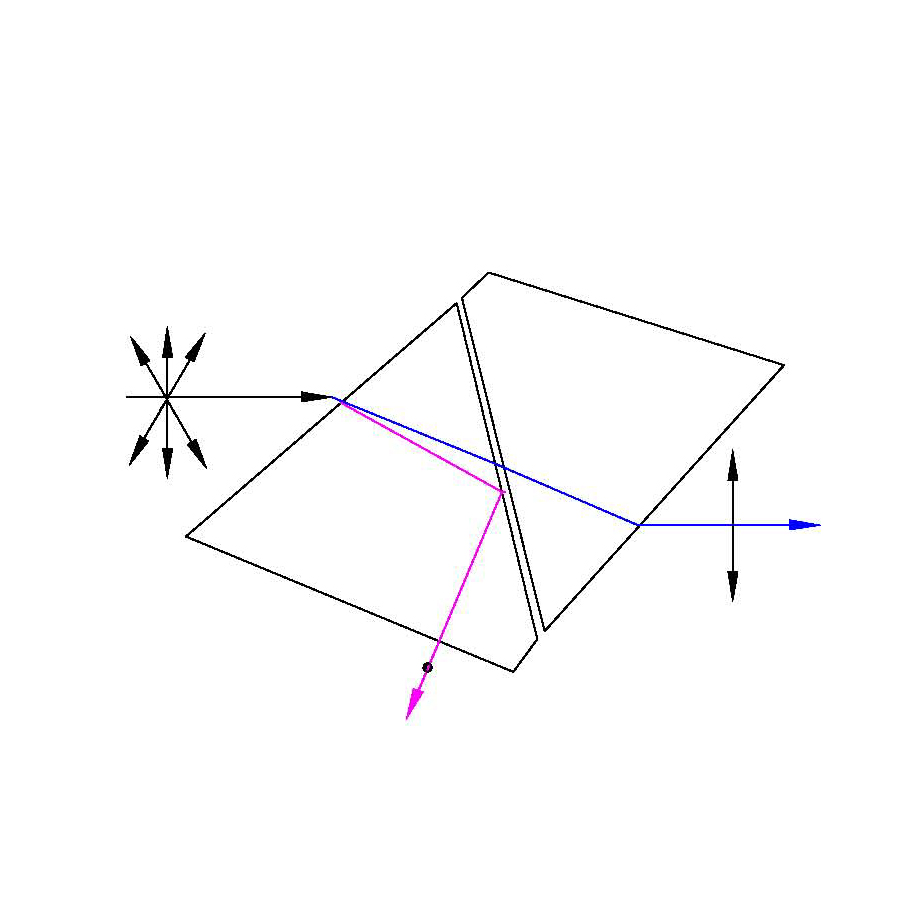
Glan-Laser Prism Polarizer |
Calcite(350~2300nm)α-BBO (190~3500nm)YVO4 (500~4000nm) |
|
Air-SpacedNear Brewster CuttingWith escape windowapplicable for high Damage energy |
Glan-Thompson Polarization Prism |
Calcite(350~2300nm)α-BBO(190~3500nm) |
|
CementedNot applicable forHigh Damage thresholdWide acceptance angle |
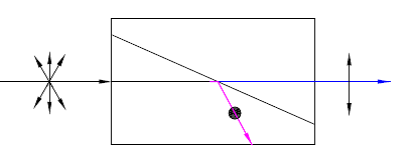
Brewster Polarizer |
Calcite(350~2300nm)YVO4(500~4000nm) |
|
High Transmisson: Tp>98%High Damage ThresholdNot need AR coating |
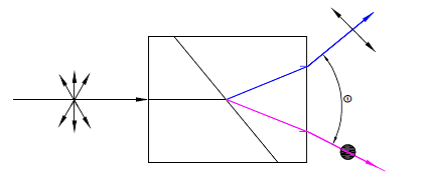
Wollaston Prism Polarizer |
Calcite(350~2300nm)Quartz(200~2300nm)YVO4(500~4000nm) |
|
Cemented or Optical contactedSeperating O and E by a specified angle |
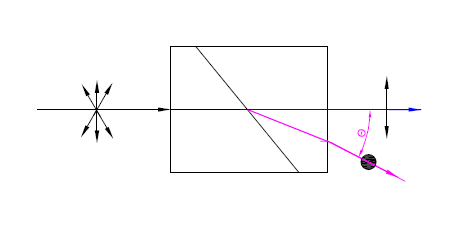
Rochon Prism Polarizer |
Quartz(200~2300nm)α-BBO(190~3500nm)YVO4(500~4000nm) |
|
Cemented or Optical contactedSeperating O and E by a specified angleJust O beam deflected
|
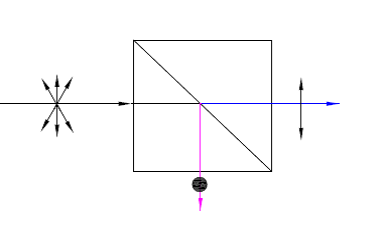
Polarization Beamsplitter Cubes |
K9(350~2000nm)ZF2(400~2000nm) |
|
Separate O and E by 90° |
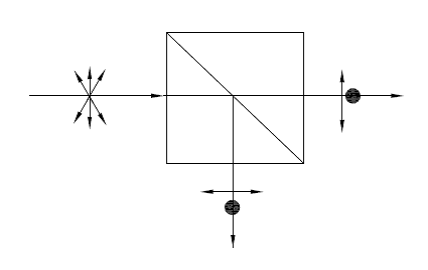
Non Polarization Beamsplitter |
K9(350~2000nm) |
|
Separate O and E equally |